Hierarchical Temporal Logic Specifications for Robotic Tasks
Overview:
Conventional robotic planning, whether task or motion planning, primarily focuses on guiding a robot from an initial state to a target state while avoiding unsafe scenarios. However, with advancements in robotic technology, robots are increasingly expected to perform more complex tasks that go beyond simple point-to-point objectives. For example, a human might ask a robot to “refill my cup,” with tasks such as “refill a cup with Coca or Sprite” or “wash the cup before refilling it.”
In this project, we explore the use of temporal logic specifications—a formalism capable of expressing such temporal and logical constraints. While temporal logic is expressive, its existing forms are often computationally inefficient, limiting the scalability of decision-making algorithms for complex tasks. This challenge motivates us to address the following research objectives:
Design user-friendly temporal logic specifications that can enable computationally efficient decision making.
Bridge the gap between human's daily use of language and the task specification to achieve intuitive human-robot interaction.
Research Topics
Decision Making under Hierarchical Temporal Logic Specifications
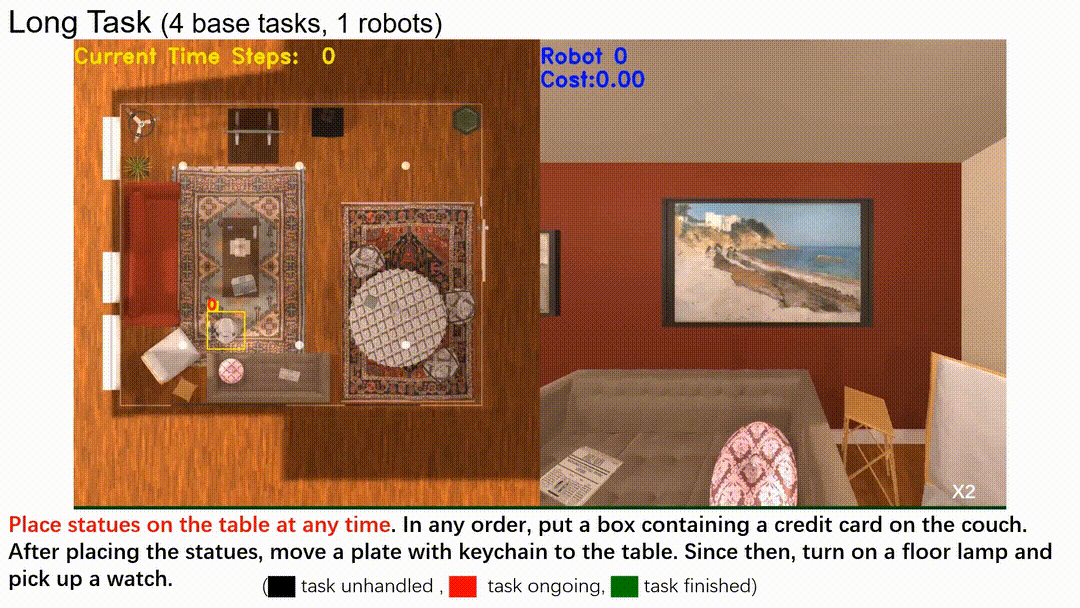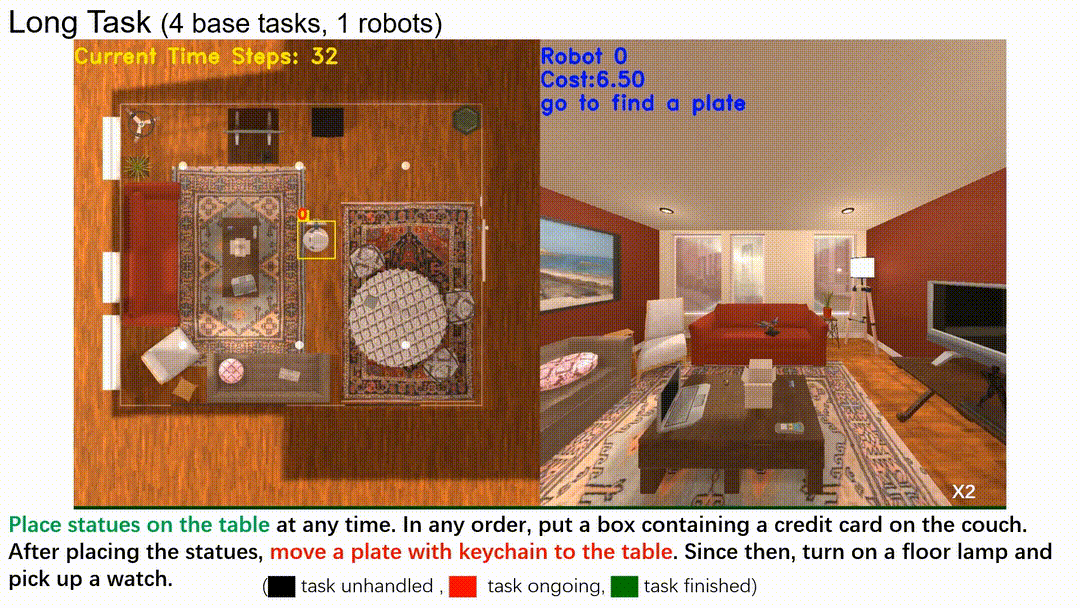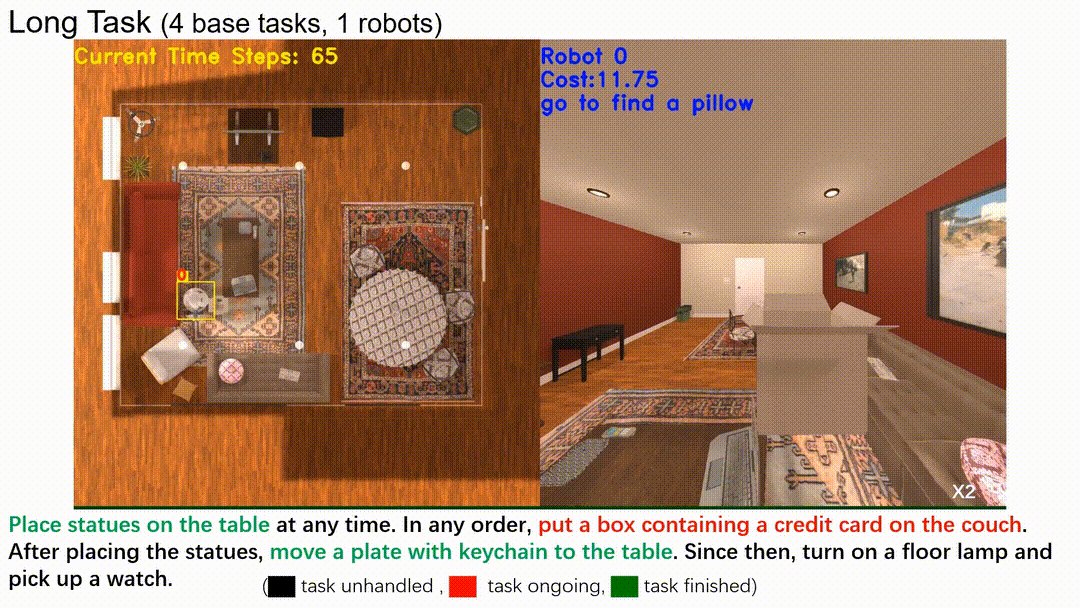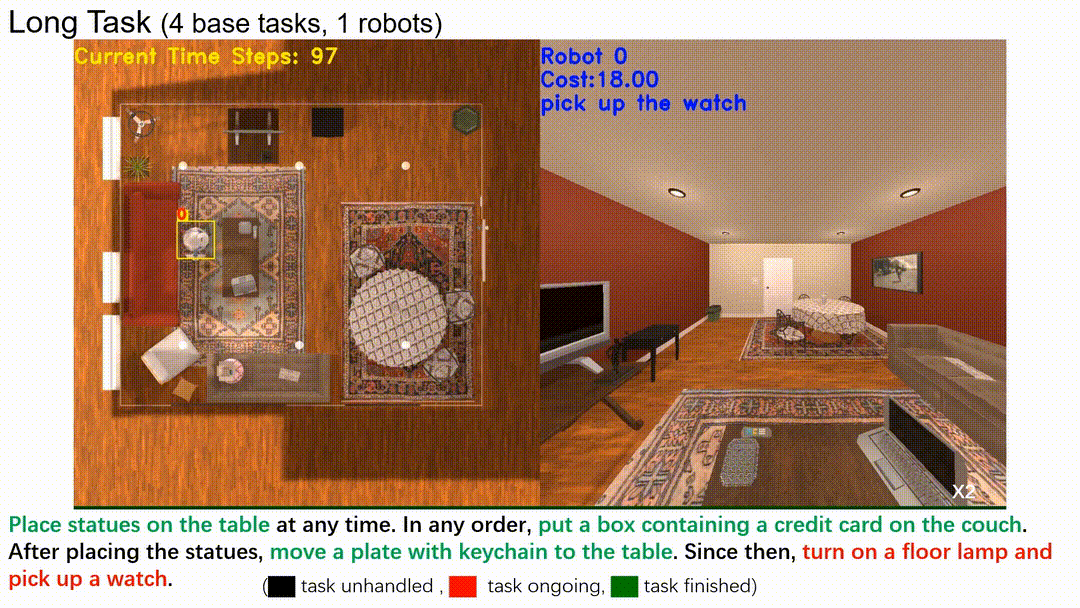
In this line of work, we introduce a hierarchical structure to temporal logic specifications, encompassing both syntax and semantics, and demonstrate that it is more expressive than traditional flat specifications. A user study comparing flat and hierarchical specifications revealed that users found the hierarchical structure significantly easier to understand when dealing with complex tasks. Building on these expressive task specifications, we developed planning algorithms tailored for multi-robot systems, seamlessly integrating task allocation into the planning process.
Publications:
-
[J33] Simultaneous Task Allocation and Planning for Multi-Robots under Hierarchical Temporal Logic Specifications
Xusheng Luo and Changliu Liu
IEEE Transaction on Robotics, 2025
-
[J25] Decomposition-based Hierarchical Task Allocation and Planning for Multi-Robots under Hierarchical Temporal Logic Specifications
Xusheng Luo, Shaojun Xu, Ruixuan Liu and Changliu Liu
IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2024
Translating Instructions to Hierarchical Temporal Logic
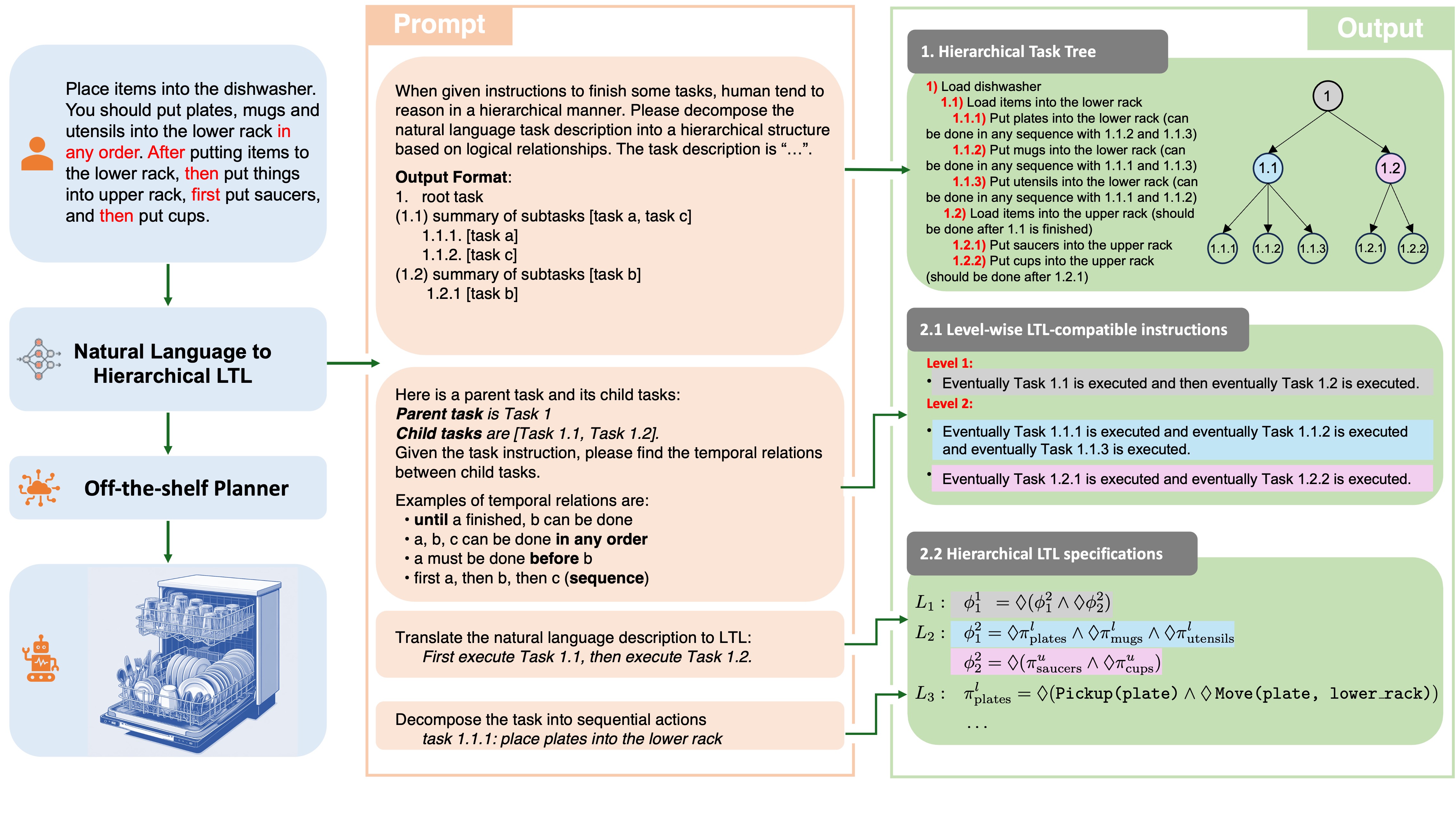
To enable non-experts to specify long-horizon, multi-robot collaborative tasks, language models are increasingly used to translate natural language commands into formal specifications. However, because translation can occur in multiple ways, such translations may lack accuracy or lead to inefficient multi-robot planning. Our key insight is that concise hierarchical specifications can simplify planning while remaining straightforward to derive from human instructions. We propose Nl2Hltl2Plan, a framework that translates natural language commands into hierarchical Linear Temporal Logic (LTL) and solves the corresponding planning problem.
Contributors: Shaojun Xu, Xusheng Luo, Yutong Huang, Letian Leng, Ruixuan Liu
Contributors: Shaojun Xu, Xusheng Luo, Yutong Huang, Letian Leng, Ruixuan Liu
Publications:
Period of Performance: 2023 ~ Now
Point of Contact: Xusheng Luo
